 Effective power Effective power
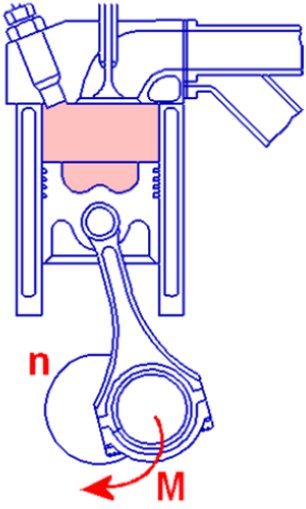
The piston accelerates from zero to approximately 100 km/h in 2.5 milliseconds. Compared to the absolute most powerful sports cars, that would be more than a thousand times the acceleration. Now you can perhaps
guess why every gram of unnecessary piston weight is gladly saved and why any differences between the pistons are combated down to almost the last gram.
Of course, we did not calculate the entire curve above, but only the maxima and minima. If you assume that the length of the connecting rod l is not too long at 130 mm, you can now do this for
every point of the curve. You can see that the second part of the parenthesis forms a kind of correction for the intermediate positions.
This part in parentheses also explains why no equal sign is used in the equation. It is part of a binomial series that has been truncated after the second order. So,
a simplification has been created to make calculation easier, but it only distorts the calculation result insignificantly.
Oh yes, then there's the dot above the 's'. It is often used when looking at a value over time. It's just meters per second that result for the respective piston speed. For example, instead of the label 'v' for driving speed, you
could also use an 's' with a dot as distance over time.
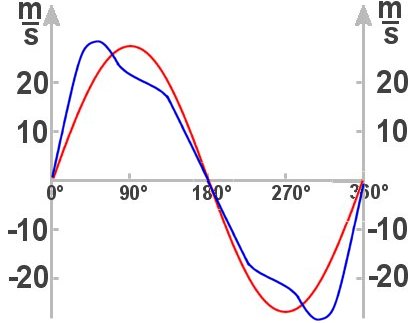
The connecting rod length l is also important for the lay out design of an engine. Actually, you would like to keep it as short as possible because it determines the height of the engine. However, the image above shows that
the shortest possible connecting rods (blue curve) not only shift the point of maximum piston speed forward, but can even increase it.
The considerations made so far relate more to the durability of the reciprocating piston engine and its vibration behavior. Let's now turn our attention to the not insignificant power output of the
engine. One thing must be clear: power is generated from torque and engine speed:
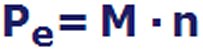
By the way, the lowercase 'e' stands for 'effective', which is used in the same way as it is in real life. So, what actually comes out at the rear, i.e., at the clutch. The importance of torque cannot be overstated. Suffice it to say
that it depends directly on the piston force, which in turn depends on the pressure on the piston:

But what does the pressure in the cylinder depend on? Since it is produced by the combustion of a certain amount of a mixture of air and fuel, this should be as large as possible if the ratio and mixing are optimal. If it
reaches the combustion chamber only by suction, then its size or displacement is decisive. At this point, it should be noted once again that combustion chamber and displacement are not the same thing.
|