 Air Mass Sensor 1 Air Mass Sensor 1
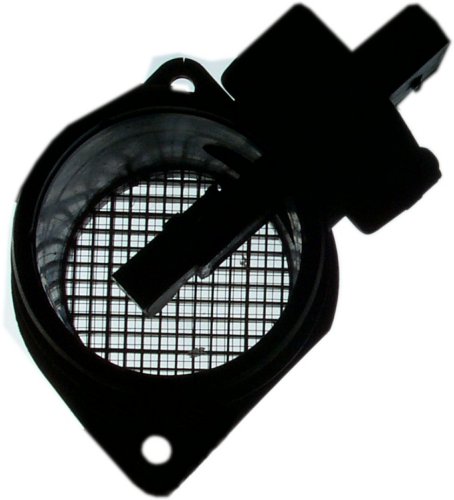

Today we try to avoid sensors where something moves and which are therefore subject to wear and tear. That is why the dynamic pressure air flow meter soon became megaout (for picture see chapter Potentiometer).
Today we are two generations ahead, namely with the hot film as successor of the hot wire air mass meter.
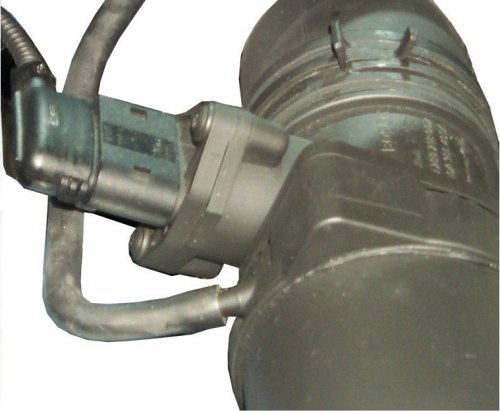

You can already see that, apart from the absence of moving parts, there is another common feature between these two, namely heating. As the name of the older of the two says, here a wire is electrically heated. All the air
flowing through, while in the younger one a film on a small ceramic heats up only a small fraction (measuring in bypass).
The hot wire caused problems. It costs energy, which was added to the intake air, but was rather undesirable in the engine. The intake air should be as cold as possible and contain a lot of oxygen. In addition, the wire had to
be burnt free at about 1,000°C after the engine was switched off, so that no residues would disturb the operation next time.
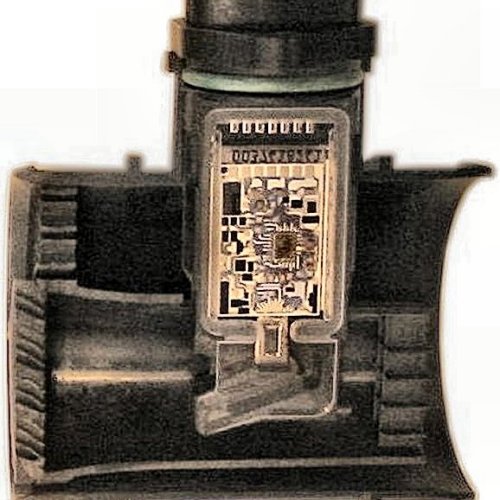

Accordingly, the subsequent construction used much less energy. You can see it in the picture above. A small part of an altogether already calmed (large diameter) on the left is taken off and some of it gets into the opening
to a small channel, which leads to the heating element after a curve. The type of measurement is the same as the previous one.
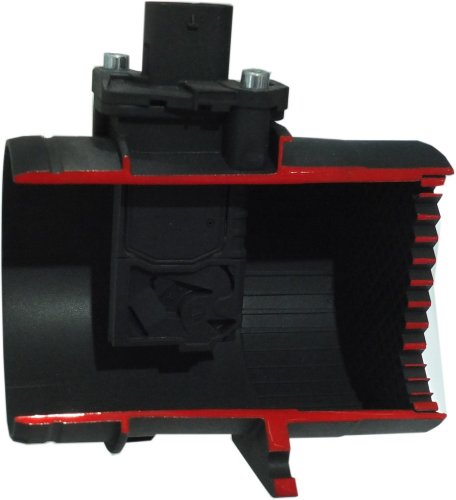

Basically, a platinum hot wire or the resistor, also made of platinum, heats the air. When a certain temperature is reached, the heating current is reduced. It therefore remains constant, monitored by a temperature-dependent
resistor. Here we are still dealing with analogue technology. The whole circuit is called a 'Wheatstone Bridge'.

Thus it is possible that a constant temperature by the also known as temperature compensation sensor is set directly behind the hot film, even if the cooling air mass increases until full load. Of course, the power supply
must increase for this. Its voltage is registered and forms a measure for the control unit of the air mass flowing through it.

The great age of the air flow meter is actually long gone, at least for petrol engines, because a large part of its importance has been transferred to the lambda sensor. Because only one sensor may send data to the control
unit which will cause it to grease or slim down. In principle, the air mass meter is only asked for as long as the lambda sensor is not yet able to work e.g. in cold conditions or during acceleration, when enrichment is
required.
Just how strong the pulsations in the intake system are is shown by a problem that has been occurring for years in BMW four-cylinder engines. Here it could happen that back and forth air flows were measured twice. This
prevents nowadays the reverse current detection. By comparing the temperature before and after the actual measurement, returning or already existing air flows can be reliably detected at the difference.
|