
|
Single-spark Coil
| Dormant high-tension distribution |
| Cylinder-selective, more resistant to errors, with more reserve |
It completely cancels out problems with the sometimes interference-prone high tension cables and increases the ignition voltage reserve. In relation to multiple ignitions the shorter charging periods are important. In the
case of knocking tendency, compared to the double-spark ignition coil, the cylinder-selective shifting of ignition points is possible. Nowadays, in contrast to the earlier devices, which
completely separated the primary- and secondary windings, the errors are not transmitted from one system to the other.
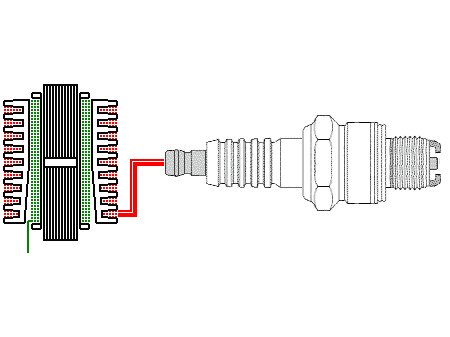
The ignition coil construction is integrated into a somewhat longer spark plug cap. The controlling is carried out in each case, from terminal 1 (picture above) at the bottom left shown in green. Each single-spark coil has
one. The large part in the center, shown in black, is the soft-iron core. The secondary winding (red) is integrated into a cooler. This leads, through a short connection, directly to the spark plug. As can be seen in the picture
below, there are in the meantime, two switching possibilities: - from the secondary winding directly to earth and through a resistance to earth and from terminal 4a to the conrol device (secondary circuit monitoring).
Compared with the above described compact ignition coil, the pencil coil (picture 3) is almost as thin and no part of the coil sticks out from the cylinder head. All the parts are arranged lengthwise starting directly above the
spark plug. Inside, first of all, the magnetizable sheet-metal core, tightly wound around the core is the bobbin with the secondary windings and concentric, needing very little space, the primary windings. In the assembly
and fitting into the plastic casing, impregnating resin for the durability and silicone for the insulation are used for both construction forms. A disadvantage is, with this limited amount of space one has only very little
adjustment freedom.
| Measuring technology of the single-spark coil is more complicated.. |
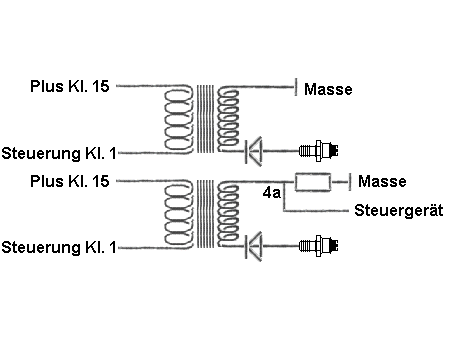
The single spark coil provides the spark plug with between 15.000 and 45.000 V of high tension. Voltage muliplying diodes on the secondary side prevent that, when the magnetic field is switched on, through induction an
ignition spark jumps across resulting in an unwanted combustion. These diodes, depending on the material, have e.g., a breakdown voltge of 500 V each. Ten of them in a row having the same lockout direction, would be
sufficient to 'brake' an unwanted ignition tension by 5000 V. This circuit makes a resistance test impossible. However, voltage measuring is possible on terminal 4a (picture above), taking the tension division between the
coil
and the diodes into account. 08/11
|
|