Starter (additional information)
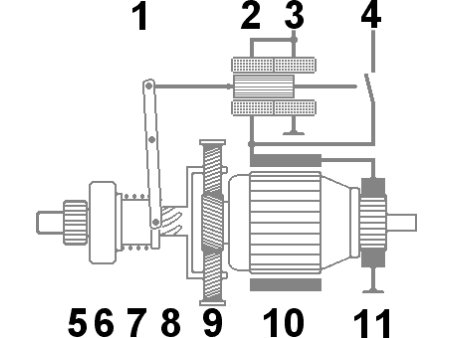
| Number | Part |
| 1 | Pinion-engaging lever |
| 2 | Pull-in winding |
| 3 | Hold-in winding |
| 4 | Electric switch (large cross-section) |
| 5 | Pinion |
| 6 | Over-running clutch |
| 7 | Meshing spring |
| 8 | Helix |
| 9 | Speed reducer (planetary gear) |
| 10 | Armature and inductor coil |
| 11 | Collector |
Function
There are worldwide - except in certain utility vehicle diesel engines - only thrust-screw-drive starters built-in. This technology is used to connect an electric motor for the duration of the engine start, with the engine.
This connection should not occur by shifting the complete armature spindle and, of course, be guaranteed to work constantly without causing problems.
How it works
Just like in real life there are at least two possibilities. Either the pinion (5) of the starter motor engages through the force and lever connection of the solenoid
directly (30%
probability), or it pushes the cogs tooth to tooth onto each other. In the most favourable case the induction current (4) can be switched on shortly before the complete offset of the alignment.What happens, however, if
the pinion does not immediately find a gap? In this case the engaging arm (1) is nevertheless further pulled, compressing the meshing spring (7). The pressure on the pinion to mesh grows. If the starter motor now
starts to turn, the pinion is pushed into the next gap that comes up. The helix coil (8) protects the teeth of the flywheel a little against an all too heavy connection.
The mechanical disengagement becomes effective if while starting the engine the pinion is driven by the flywheel gearing. The solenoid is switched off and the pinion is no longer held in the flywheel gearing. Because
it is connected by the counter-rotating helix (8) with the armature spindle which now drives it, it is pulled out of the gearing. Over-revving of the electric motor is prevented by the freewheel (6),
located next to the pinion.
Because any attempt to start an already running engine makes ugly noises and also is not at all good for the mechanics, this is prevented in modern vehicles by a special circuit. The terminal-point designations in
Germany, are, apart from the earth-31 and plus-30 in the large cross sectioned switch (4), also the cable-50 from the ignition start-switch to the solenoid (No.3) and also a possible control wire to the ignition (15a).
07/08
|